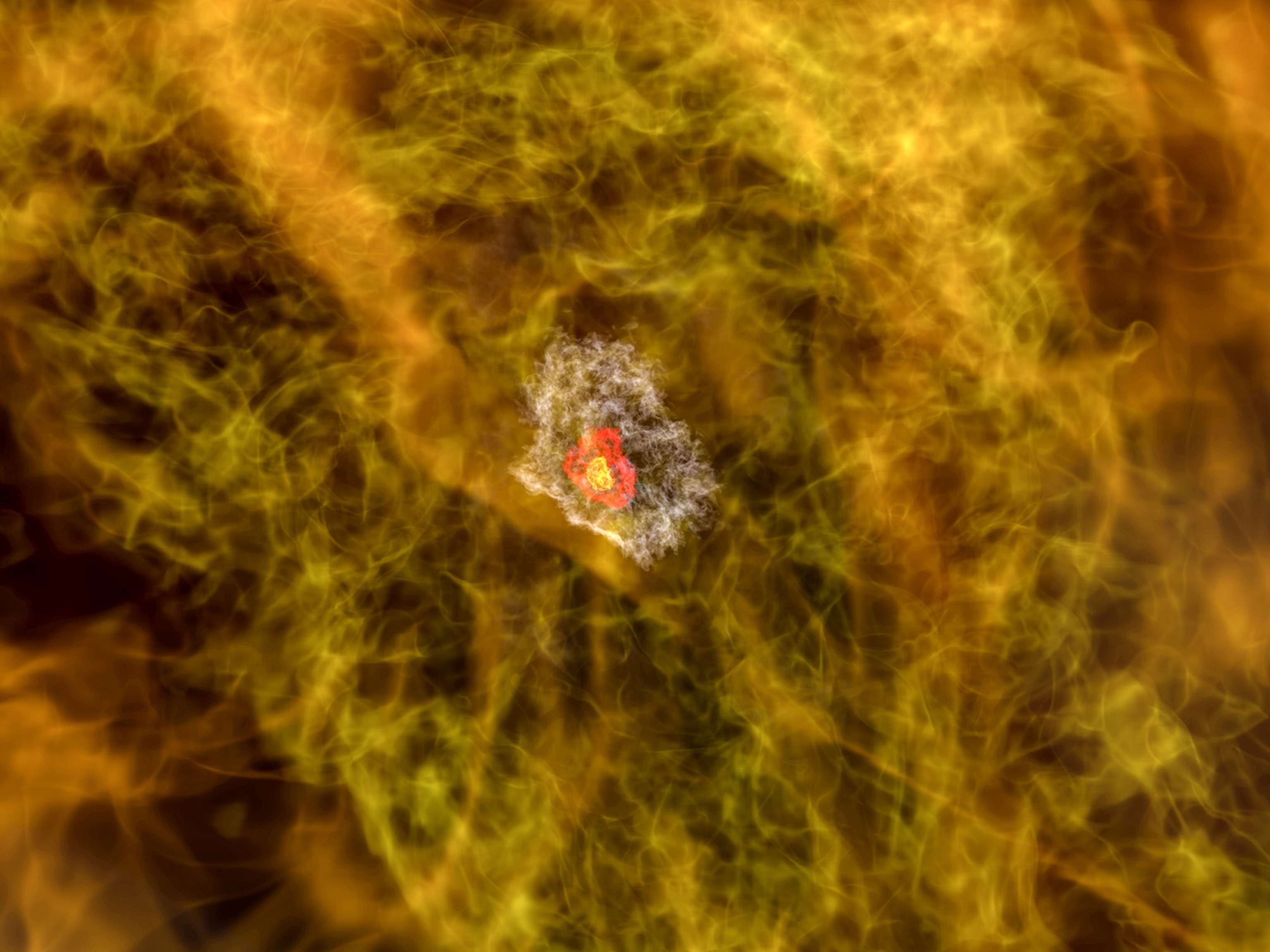
Black Holes, explained
These infinitely dense points in space will spaghettify anything that ventures too close.
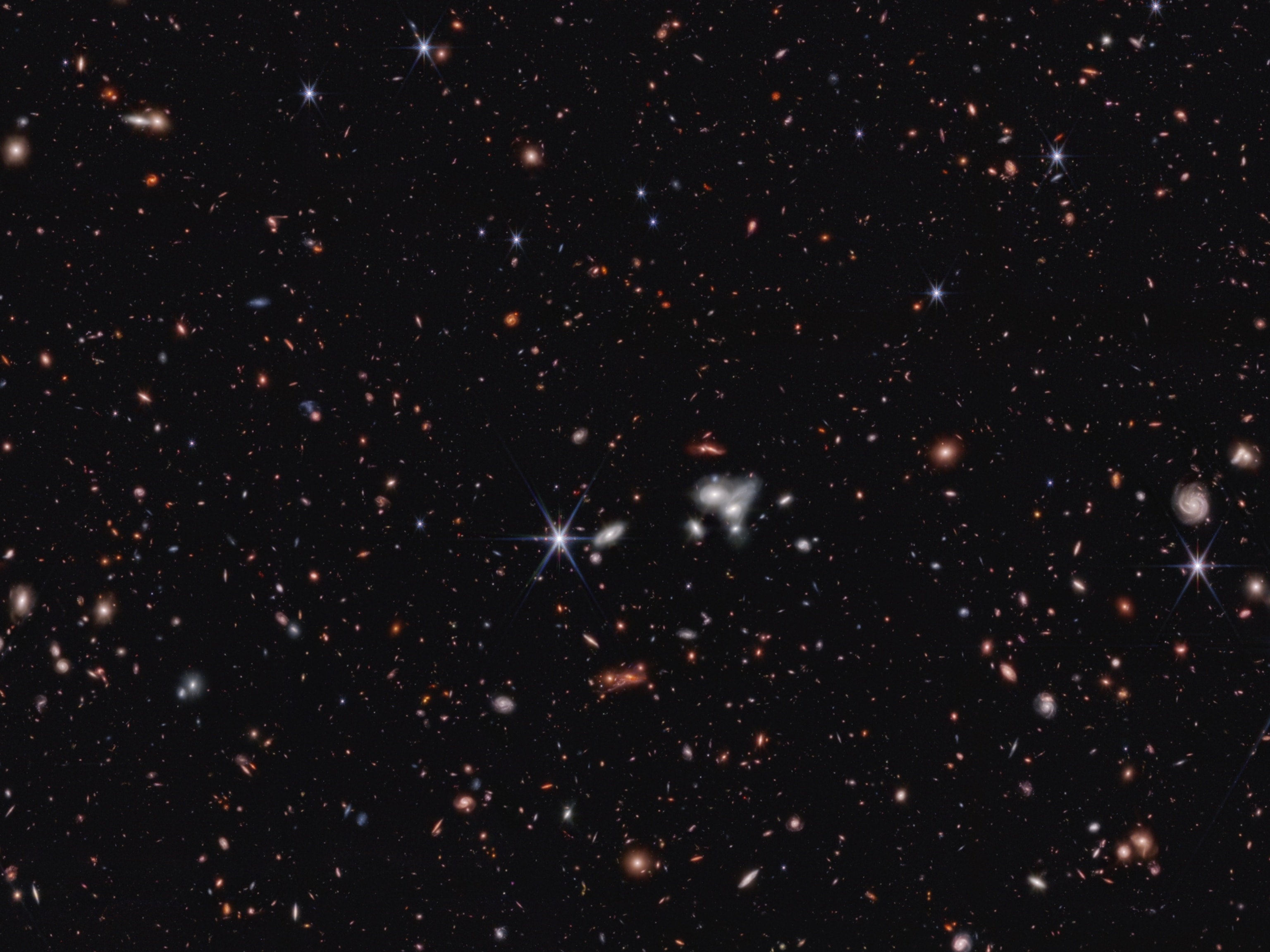
Black holes are points in space that are so dense they create deep gravity sinks. Beyond a certain region, not even light can escape the powerful tug of a black hole's gravity. And anything that ventures too close—be it star, planet, or spacecraft—will be stretched and compressed like putty in a theoretical process aptly known as spaghettification.
There are four types of black holes: stellar, intermediate, supermassive, and miniature. The most commonly known way a black hole forms is by stellar death. As stars reach the ends of their lives, most will inflate, lose mass, and then cool to form white dwarfs. But the largest of these fiery bodies, those at least 10 to 20 times as massive as our own sun, are destined to become either super-dense neutron stars or so-called stellar-mass black holes.
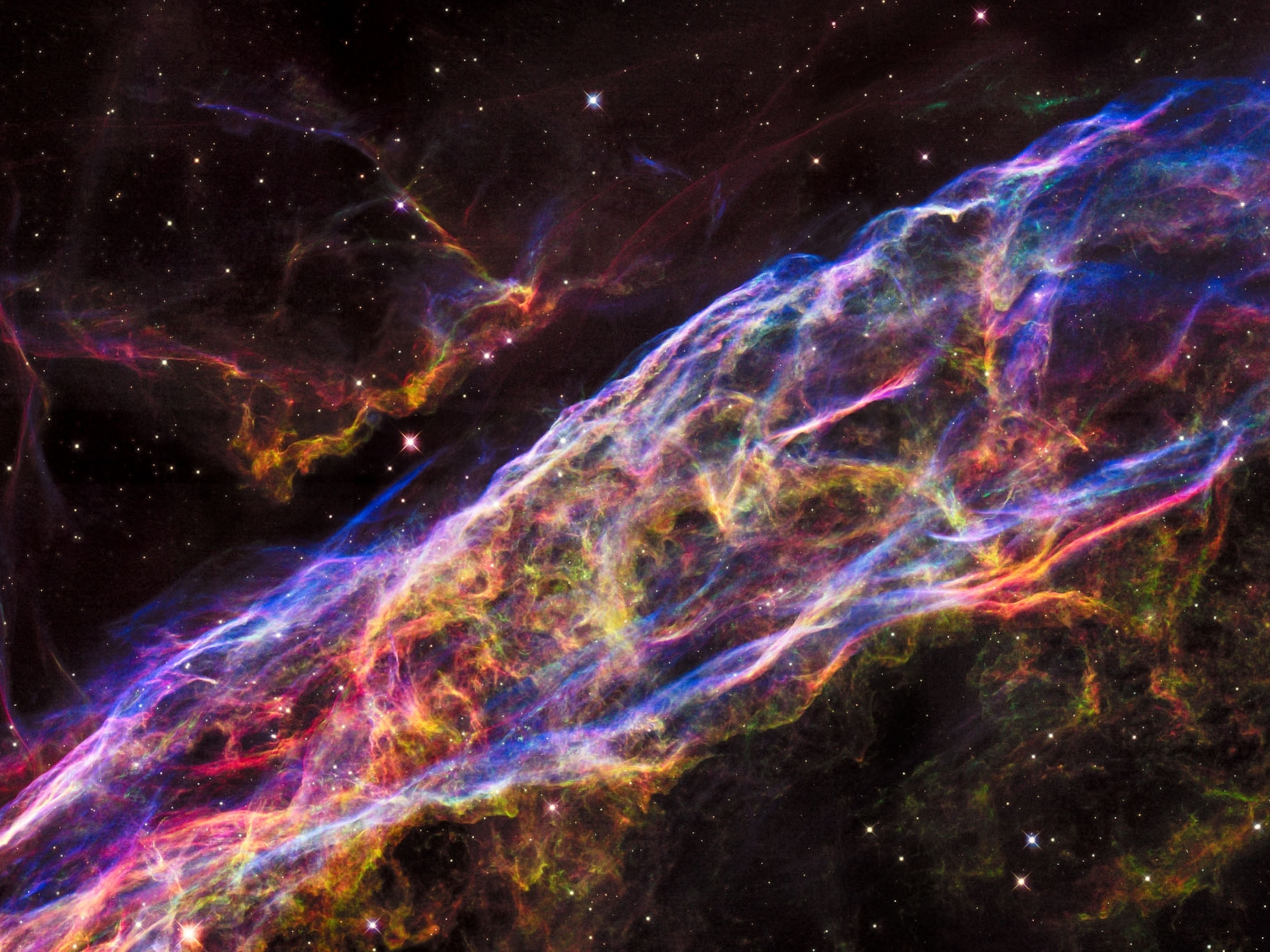
In their final stages, enormous stars go out with a bang in massive explosions known as supernovae. Such a burst flings star matter out into space but leaves behind the stellar core. While the star was alive, nuclear fusion created a constant outward push that balanced the inward pull of gravity from the star's own mass. In the stellar remnants of a supernova, however, there are no longer forces to oppose that gravity, so the star core begins to collapse in on itself.
If its mass collapses into an infinitely small point, a black hole is born. Packing all of that bulk—many times the mass of our own sun—into such a tiny point gives black holes their powerful gravitational pull. Thousands of these stellar-mass black holes may lurk within our own Milky Way galaxy.
One black hole is not like the others
Supermassive black holes, predicted by Einstein's general theory of relativity, can have masses equal to billions of suns; these cosmic monsters likely hide at the centers of most galaxies. The Milky Way hosts its own supermassive black hole at its center known as Sagittarius A* (pronounced “ay star”) that is more than four million times as massive as our sun.
The tiniest members of the black hole family are, so far, theoretical. These small vortices of darkness may have swirled to life soon after the universe formed with the big bang, some 13.7 billion years ago, and then quickly evaporated. Astronomers also suspect that a class of objects called intermediate-mass black holes exist in the universe, although evidence for them is so far debatable.
No matter their starting size, black holes can grow throughout their lives, slurping gas and dust from any objects that creep too close. Anything that passes the event horizon, the point at which escape becomes impossible, is in theory destined for spaghettification thanks to a sharp increase in the strength of gravity as you fall into the black hole.
As astrophysicist Neil Degrasse Tyson once described the process: “While you're getting stretched, you're getting squeezed—extruded through the fabric of space like toothpaste through a tube.”
But black holes aren't exactly “cosmic vacuum cleaners,” as often depicted in popular media. Objects must creep fairly close to one to lose this gravitational tug-of-war. For example, if our sun was suddenly replaced by a black hole of similar mass, our planetary family would continue to orbit unperturbed, if much less warm and illuminated.
Peering through the darkness
Because black holes swallow all light, astronomers can't spot them directly like they do the many glittery cosmic objects in the sky. But there are a few keys that reveal a black hole's presence.
For one, a black hole's intense gravity tugs on any surrounding objects. Astronomers use these erratic movements to infer the presence of the invisible monster that lurks nearby. Or objects can orbit a black hole, and astronomers can look for stars that seem to orbit nothing to detect a likely candidate. That's how astronomers eventually identified Sagittarius A* as a black hole in the early 2000s.
Black holes are also messy eaters, which often betrays their locations. As they sip on surrounding stars, their massive gravitational and magnetic forces superheat the infalling gas and dust, causing it to emit radiation. Some of this glowing matter envelops the black hole in a whirling region called an accretion disk. Even the matter that starts falling into a black hole isn't necessarily there to stay. Black holes can sometimes eject infalling stardust in mighty radiation-laden burps.
Related Topics
You May Also Like
Go Further
Animals
- How can we protect grizzlies from their biggest threat—trains?How can we protect grizzlies from their biggest threat—trains?
- This ‘saber-toothed’ salmon wasn’t quite what we thoughtThis ‘saber-toothed’ salmon wasn’t quite what we thought
- Why this rhino-zebra friendship makes perfect senseWhy this rhino-zebra friendship makes perfect sense
- When did bioluminescence evolve? It’s older than we thought.When did bioluminescence evolve? It’s older than we thought.
- Soy, skim … spider. Are any of these technically milk?Soy, skim … spider. Are any of these technically milk?
Environment
- Are the Great Lakes the key to solving America’s emissions conundrum?Are the Great Lakes the key to solving America’s emissions conundrum?
- The world’s historic sites face climate change. Can Petra lead the way?The world’s historic sites face climate change. Can Petra lead the way?
- This pristine piece of the Amazon shows nature’s resilienceThis pristine piece of the Amazon shows nature’s resilience
- Listen to 30 years of climate change transformed into haunting musicListen to 30 years of climate change transformed into haunting music
History & Culture
- Meet the original members of the tortured poets departmentMeet the original members of the tortured poets department
- Séances at the White House? Why these first ladies turned to the occultSéances at the White House? Why these first ladies turned to the occult
- Gambling is everywhere now. When is that a problem?Gambling is everywhere now. When is that a problem?
- Beauty is pain—at least it was in 17th-century SpainBeauty is pain—at least it was in 17th-century Spain
Science
- Here's how astronomers found one of the rarest phenomenons in spaceHere's how astronomers found one of the rarest phenomenons in space
- Not an extrovert or introvert? There’s a word for that.Not an extrovert or introvert? There’s a word for that.
- NASA has a plan to clean up space junk—but is going green enough?NASA has a plan to clean up space junk—but is going green enough?
- Soy, skim … spider. Are any of these technically milk?Soy, skim … spider. Are any of these technically milk?
Travel
- Dina Macki on Omani cuisine and Zanzibari flavoursDina Macki on Omani cuisine and Zanzibari flavours
- How to see Mexico's Baja California beyond the beachesHow to see Mexico's Baja California beyond the beaches
- Could Mexico's Chepe Express be the ultimate slow rail adventure?Could Mexico's Chepe Express be the ultimate slow rail adventure?